Attributes
Cloning Attributes
Any attribute can be cloned via the Tools → Clone Attribute… menu option.
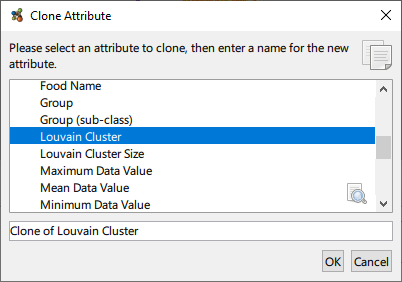
Select the attribute to be cloned and provide a name.
Editing Attributes
Some attributes can be edited. Generally speaking these are the user defined attributes that are loaded with the graph, but also includes those that are imported later. The description attached to the attribute can be modified, as can the type of the attribute, in the case where it can be interpreted multiple ways. These options are available via Tools → Edit Attribute…
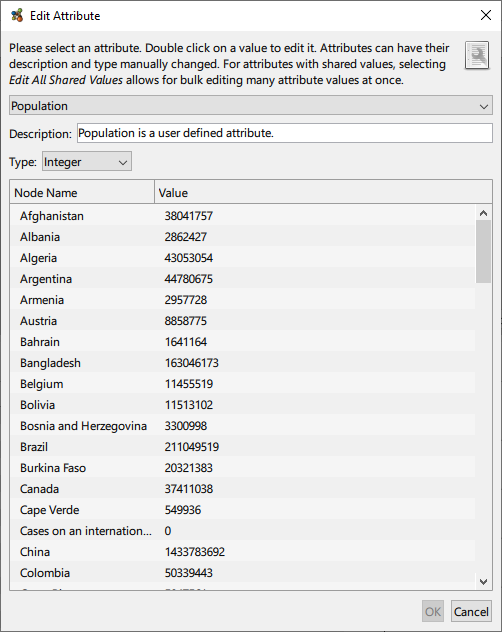
This can be used in conjunction with the clone funcionality in order to facilitate the annotation of clusters. For example, a cluster transform such as Louvain can be performed and its resulting attribute cloned. Thereafter, this cloned attribute can be edited and the Edit All Shared Values option chosen. This allows for the bulk editing of the cluster names, in this case replacing e.g. “Cluster 1” with a meaningful name that reflects its function or association within the data. Note that if the clustering parameters are subsequently altered, e.g. its granularity is changed, the manually cloned attribute with the annotation edits is not automatically updated to reflect any cluster changes.
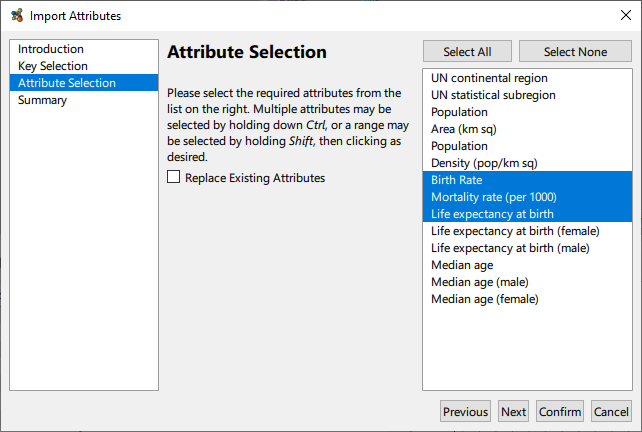
Importing Attributes
It may be that having created a graph, it is desirable to superimpose some external meta data onto the graph as attributes. This facility is available via the Tools → Import Attributes From Table… menu option. The table in question should be constructed as a simple column wise list of attribute values, with the first row providing names for the attributes. In particular, one column needs to be a key that it used to map rows in the table to nodes in the graph.
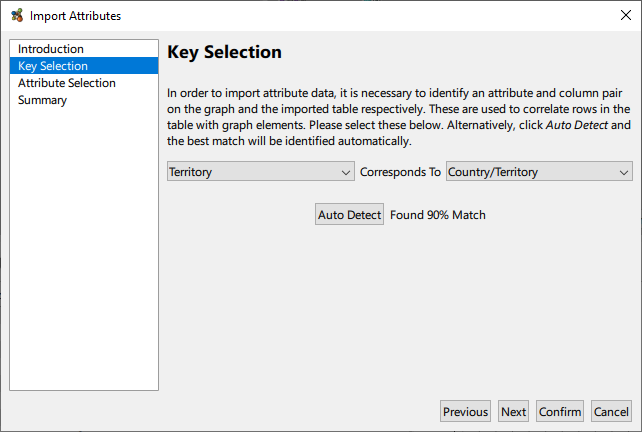
Once the key mapping is detected or selected, it only remains to select which attributes to import from the table.